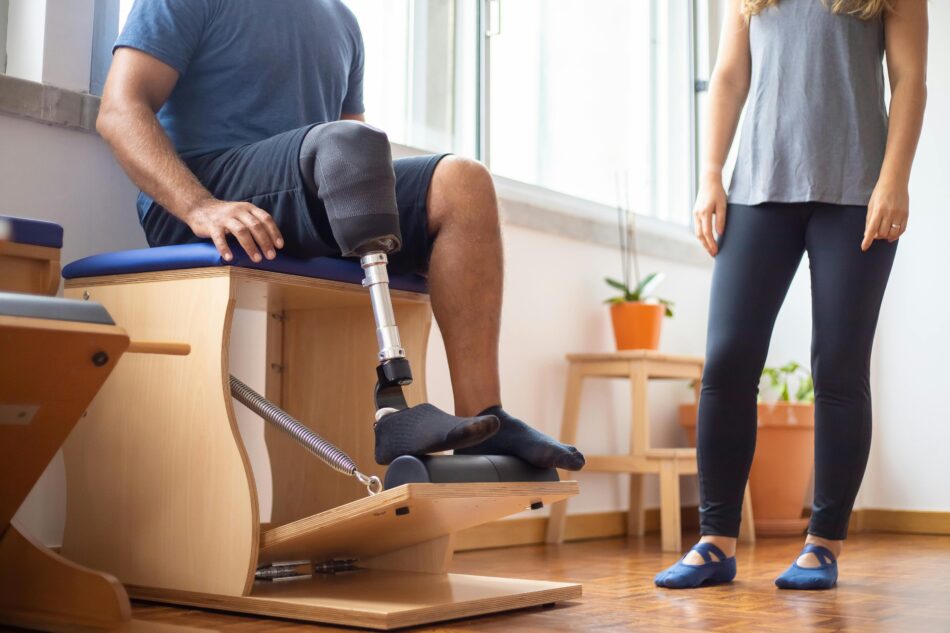
Introduction: Elevating Lives Through Effective Amputee Rehab
In the journey of recovery after limb loss, regaining function, mobility, and confidence is paramount. Mastering prosthetic use is not a one-size-fits-all process. It demands a holistic approach physical, psychological, and technical. This guide outlines a structured and expert-driven pathway to successful amputee rehabilitation, focusing on long-term independence and quality of life.
Understanding the Phases of Amputee Rehabilitation
Pre-Prosthetic Training: Foundation of Success
Before prosthetic fitting, it is critical to prepare the residual limb and the body for future prosthetic use.
- Wound healing and edema control
Proper limb care, compression therapy, and desensitization techniques reduce complications and promote healthy skin. - Muscle strengthening and range of motion
Targeted exercises prevent contractures and improve muscle balance. - Psychological support
Emotional resilience is strengthened through counseling, peer support, and patient education.
Prosthetic Fitting and Customization
Optimal prosthetic integration begins with accurate fitting and adjustment based on individual needs.
- Socket comfort and limb interface
Custom-molded sockets and liner systems enhance comfort and reduce skin breakdown. - Alignment and gait tuning
Biomechanical alignment ensures energy-efficient gait and stability. - Suspension systems and component choices
From suction to pin-lock to vacuum systems, choosing the correct suspension impacts mobility profoundly.
Mastering Prosthetic Use: Structured Training Protocol
Initial Gait Training
- Parallel bars progression
Gait initiation begins in parallel bars with support from trained therapists. - Weight shifting and balance drills
Patients practice dynamic balance, building trust in the prosthesis. - Step-over-step ambulation
Encouraging symmetric walking patterns from the earliest stages is key to long-term success.
Intermediate Skill Development
- Navigating uneven terrain and inclines
Patients develop adaptability through surface variation drills. - Stair climbing and curbs
Specific techniques vary by amputation level but are essential for community mobility. - Assistive device weaning
Gradual reduction of dependency on walkers or canes reinforces independence.
Advanced Functional Training
- Real-world simulations
Practicing in environments that mimic work, home, and community scenarios. - Sports and recreation integration
Tailored prosthetic limbs enable return to athletic pursuits, from swimming to running. - Vocational and occupational training
Reentering the workforce requires specific skill reinforcement and ergonomic adaptations.
Psychological Reinforcement and Social Reintegration
Long-term success in amputee rehab hinges not just on physical recovery, but on psychological well-being.
- Body image and self-confidence coaching
Structured programs address identity reformation and social anxieties. - Support groups and peer mentors
Learning from others who have navigated similar paths accelerates adjustment. - Family and caregiver inclusion
Engaging loved ones in the rehab process improves continuity of care at home.
Common Challenges in Amputee Rehabilitation and How to Overcome Them
| Challenge | Strategy |
| Phantom limb pain | Mirror therapy, desensitization, TENS therapy |
| Skin irritation and breakdown | Correct socket fit, regular inspection, hygiene protocols |
| Prosthetic rejection or discomfort | Regular follow-ups, re-casting, liner system adjustments |
| Psychological withdrawal | Early mental health intervention, support network activation |
Technologies Transforming Modern Amputee Rehab
- Microprocessor-controlled knees (MPKs)
Adapt to walking speed and terrain dynamically, increasing safety. - Myoelectric prostheses
Allow fine motor control via muscle signal interpretation. - Bionic limb integration
Experimental models now offer direct neural control, revolutionizing upper limb use.
Long-Term Maintenance and Ongoing Rehabilitation
Continued care is non-negotiable in successful prosthetic use.
- Regular prosthesis reviews
Components wear out and body changes occur; yearly assessments prevent complications. - Rehabilitation tune-ups
Periodic therapy sessions help maintain alignment, gait, and strength. - Community reintegration check-ins
Ensuring access to resources, adaptive tools, and social opportunities maintains progress.
Conclusion: Empowerment Through Structured Rehabilitation
The path to mastering prosthetic use is multifaceted. Through expert-guided amputee rehabilitation, individuals not only regain physical independence but rebuild their identities and reclaim their place in the world. Each phase whether medical, technical, or psychological is essential and must be integrated into a cohesive, patient-centered strategy for sustainable success.