Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common yet often overlooked dental issue. In its early stages, it may not cause noticeable pain or discomfort, which is why many people don’t realize they have it. However, if left untreated, gum disease can lead to severe oral health problems, including tooth loss. Fortunately, with early detection and proper care, gum disease can be prevented or treated effectively.
In this blog, we will explore the early signs of gum disease, its stages, and most importantly, the preventive measures you can take to protect your gums and teeth. We will also discuss how seeking help from a professional Dentist can be crucial in managing and preventing gum disease.
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that surround and support your teeth. It is usually caused by the buildup of plaque — a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth and gums. If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which is difficult to remove without professional cleaning. This accumulation of plaque and tartar can lead to inflammation and infection of the gums, resulting in gum disease.
There are two main stages of gum disease:
- Gingivitis – The earliest stage of gum disease, gingivitis is characterized by inflammation and irritation of the gums. It is usually caused by plaque buildup on the teeth near the gum line. At this stage, the condition is often reversible with good oral hygiene practices.
- Periodontitis – If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis. This stage involves more severe damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Periodontitis can lead to the formation of pockets between the gums and teeth, which can harbor bacteria and lead to further damage. At this point, professional dental treatment is required to manage the disease.
Early Signs of Gum Disease
Being aware of the early signs of gum disease is crucial for preventing its progression. Since gum disease often develops slowly, many people may not notice it until it has advanced. Here are the common early signs to watch for:
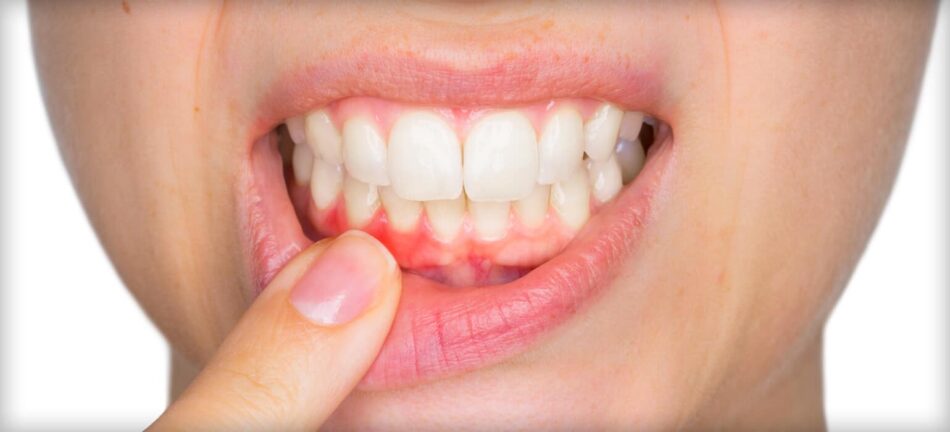
- Red, Swollen, or Bleeding Gums
One of the first signs of gum disease is red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If you notice blood while brushing or flossing, it could indicate that your gums are inflamed due to plaque buildup. Healthy gums should be firm and pale pink, not red or swollen. - Bad Breath
Persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be a sign of gum disease. The bacteria present in plaque and tartar emit foul odors that can lead to chronic bad breath. If you notice that brushing your teeth does not help freshen your breath, it could be time to check for other signs of gum disease. - Tender Gums
Gums that are tender to the touch or that hurt when you chew can be a sign that the tissues are inflamed or infected. If your gums are painful, it’s important to see a Dentist St Kilda as soon as possible to prevent further complications. - Receding Gums
Receiving gums, where the gum tissue pulls back from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth or even its root, is another common sign of gum disease. This condition can cause tooth sensitivity, especially to hot and cold temperatures. Receding gums also create pockets where bacteria can thrive, worsening the infection. - Loose Teeth
In more advanced stages of gum disease, the loss of bone and tissue that support the teeth can cause teeth to become loose. This is a serious symptom of periodontitis and requires immediate attention from a dentist. - Changes in the Fit of Dentures or Bridges
If you wear dentures or bridges and notice that they no longer fit correctly, it could be due to gum recession or bone loss caused by gum disease. If this happens, it is important to consult your dentist for an examination.
Causes of Gum Disease
Understanding what causes gum disease can help you take steps to prevent it. Some of the most common causes include:
- Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing are the primary causes of gum disease. When you don’t remove plaque from your teeth, it hardens into tartar, which can lead to gum inflammation and infection. - Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking and tobacco use are major risk factors for gum disease. The chemicals in tobacco can reduce blood flow to the gums, impair immune function, and contribute to the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth. - Poor Diet
A diet low in essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C, can weaken your immune system and make it harder for your body to fight infections, including gum disease. A poor diet can also lead to obesity, which increases the risk of developing gum disease. - Genetics
Some people are more genetically predisposed to gum disease. If you have a family history of periodontal disease, you may be at higher risk of developing it. - Certain Medical Conditions
Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and autoimmune diseases can make you more susceptible to gum disease. These conditions can affect your body’s ability to fight infections and maintain healthy gums. - Medications
Certain medications can contribute to gum disease by reducing saliva production or causing gum inflammation as a side effect. If you are taking medications, consult your dentist about potential oral health risks.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Prevention is key to maintaining healthy gums and teeth. Here are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing gum disease:
- Brush and Floss Regularly
The foundation of preventing gum disease is good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline. Consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash to help kill bacteria and reduce plaque buildup. - Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Regular dental check-ups are essential for preventing gum disease. A St Kilda Dentist can monitor your gum health and perform professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar that you may have missed with at-home care. Your dentist will also screen for signs of gum disease and provide early intervention if needed. - Quit Smoking
Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for gum disease. If you smoke or use tobacco products, quitting can significantly improve your gum health and reduce your risk of developing gum disease. Talk to your doctor for resources and support to help you quit. - Eat a Balanced Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients that support gum health. Make sure to get plenty of vitamin C, which is important for collagen production and gum tissue repair. Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods, as they can contribute to plaque buildup and tooth decay. - Manage Stress
Stress can weaken your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections like gum disease. Practice stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or exercise to support your overall health and oral hygiene. - Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush
A hard-bristled toothbrush can damage your gums and lead to recession. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to gently clean your teeth and gums without causing irritation or harm.
Treatment for Gum Disease
If gum disease is detected early, it can often be treated and reversed. Treatment options for gum disease may include:
- Scaling and Root Planing: A deep cleaning procedure where plaque and tartar are removed from below the gumline, and the roots of the teeth are smoothed to promote healing.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control infection and reduce inflammation.
- Surgical Procedures: In advanced cases of periodontitis, surgical treatments may be necessary to repair damaged gums and bone.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a common yet preventable condition that can have serious consequences for your oral health. By recognizing the early signs of gum disease, such as swollen or bleeding gums, bad breath, and gum recession, you can take action to prevent its progression. Practicing good oral hygiene, eating a balanced diet, and visiting your Dentist regularly are crucial steps in maintaining healthy gums and teeth.
If you notice any signs of gum disease, don’t wait—seek professional help from a dentist. With early intervention and proper care, gum disease can be effectively managed, ensuring a healthy smile for years to come.