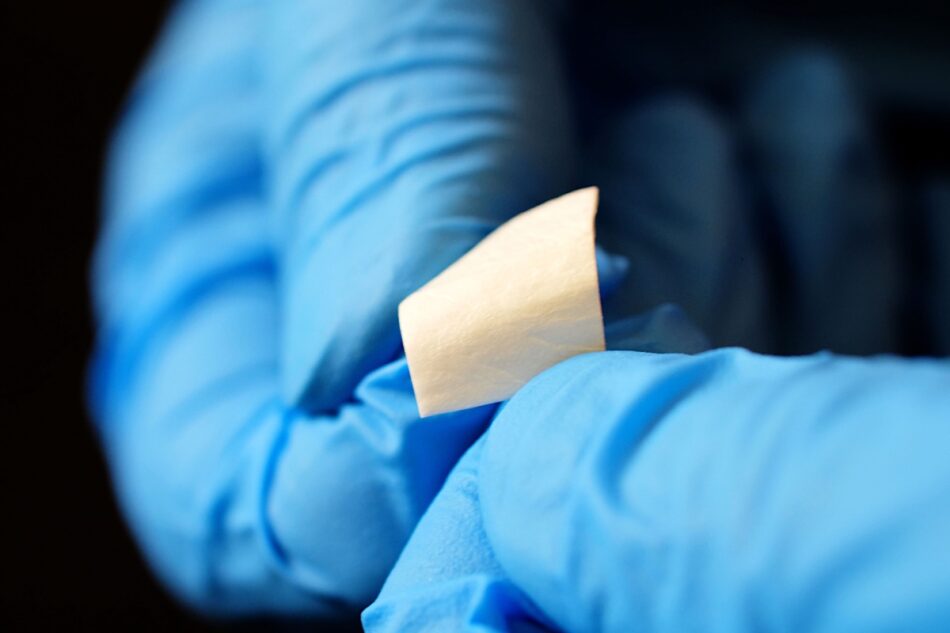
Regenerative medicine is reshaping how we approach healing, offering patients faster recovery and improved outcomes for injuries, wounds, and degenerative diseases. Among the most groundbreaking innovations in this field are amniotic grafts and amniotic membrane allografts. These biologically active materials, derived from the amniotic membrane of the placenta, are rich in natural growth factors and structural proteins that promote tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and restore normal function.
By harnessing the body’s natural regenerative potential, amniotic-based therapies are transforming modern wound care, surgical recovery, and tissue repair. Let’s explore how these two advanced materials are revolutionizing the landscape of regenerative medicine.
Understanding Amniotic Grafts
Amniotic grafts are biological coverings made from the amniotic membrane — the inner layer of the placenta that surrounds and protects the developing fetus. This membrane is a powerful natural healing material composed of collagen, fibronectin, elastin, hyaluronic acid, and a range of cytokines and growth factors.
When applied to wounds or surgical sites, amniotic grafts act as biological scaffolds that support the body’s healing processes. They provide an optimal environment for cell migration, tissue regeneration, and new blood vessel formation, while reducing inflammation and pain.
Amniotic grafts are commonly used in:
-
Chronic wound management (such as diabetic and venous ulcers)
-
Burn and trauma care
-
Orthopedic and sports medicine procedures
-
Ophthalmic surgeries
-
Plastic and reconstructive surgery
Because these grafts are derived from donated, healthy amniotic tissue (typically collected after elective cesarean deliveries), they are ethically sourced and processed under strict safety standards. The result is a biocompatible, sterile, and highly effective regenerative material.
What Is an Amniotic Membrane Allograft?
An amniotic membrane allograft is a specific type of biologic implant created from the same amniotic tissue but prepared in a way that preserves its structural and biological integrity. The term allograft refers to tissue transplanted from a donor to a genetically non-identical recipient of the same species — in this case, human-to-human.
Amniotic membrane allograft retain key biological components that make them exceptional for healing. They contain a rich extracellular matrix and bioactive molecules such as:
-
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) – stimulates epithelial cell growth
-
Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-β) – regulates tissue remodeling
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) – promotes angiogenesis and fibroblast activity
-
Interleukins and Cytokines – reduce inflammation and pain
When applied to damaged tissue, an amniotic membrane allograft supports natural regeneration by guiding new cell growth, reducing scar formation, and creating a protective barrier that fosters rapid healing.
The Regenerative Power of Amniotic Tissue
Both amniotic grafts and amniotic membrane allografts share one key advantage: their biological compatibility. Unlike synthetic grafts, amniotic tissue integrates seamlessly with the patient’s body without triggering immune rejection. This makes it particularly valuable in cases where traditional grafting methods have failed or where inflammation and infection pose major risks.
Amniotic tissue is immunologically privileged, meaning it carries minimal risk of rejection. Its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties further enhance safety and reduce the need for long-term medications or antibiotics.
Moreover, the amniotic membrane promotes angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), which improves oxygen and nutrient supply to damaged tissues, accelerating the body’s healing cycle.
Key Benefits of Amniotic Grafts and Membrane Allografts
1. Accelerated Healing
Growth factors and stem cell–supportive molecules within the amniotic membrane stimulate tissue regeneration, allowing wounds and surgical sites to heal faster and more completely.
2. Reduced Inflammation and Pain
Natural anti-inflammatory cytokines in amniotic tissue help reduce swelling, discomfort, and the formation of fibrotic scar tissue.
3. Antimicrobial Protection
Amniotic membranes possess innate antimicrobial properties that inhibit bacterial growth and reduce infection risk.
4. Minimal Immune Rejection
Due to their immunologically privileged nature, amniotic grafts and allografts integrate well with host tissues, lowering the risk of rejection or adverse reactions.
5. Improved Functional Recovery
In orthopedic and soft-tissue applications, patients often experience improved joint mobility, reduced scarring, and faster return to normal activity.
Clinical Applications Across Medical Fields
The versatility of amniotic grafts and amniotic membrane allografts has made them invaluable tools across several medical disciplines:
-
Wound Care: Used for chronic and complex wounds such as diabetic ulcers, venous ulcers, and pressure sores, where conventional dressings are ineffective.
-
Orthopedics: Applied in tendon and ligament injuries to promote tissue repair and reduce recovery times.
-
Ophthalmology: Used to treat corneal defects, chemical burns, and post-surgical healing.
-
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery: Improves graft acceptance, minimizes scarring, and supports aesthetic recovery.
-
Podiatry: Assists in repairing soft-tissue injuries and non-healing foot ulcers.
Clinical studies continue to demonstrate superior healing rates and lower complication risks when amniotic-based products are used alongside traditional treatments.
Scientific Backing and Research Evidence
A growing body of scientific literature supports the use of amniotic grafts and amniotic membrane allografts in regenerative medicine. Studies show they accelerate wound closure, reduce inflammation, and improve overall healing quality. In diabetic wound patients, for instance, amniotic membrane therapy has been linked to faster healing times and fewer amputations compared to conventional methods.
Additionally, ongoing research explores combining amniotic tissues with stem cell therapy and biologic scaffolds to further enhance regenerative outcomes. This hybrid approach could unlock new possibilities in tissue engineering and organ regeneration.
The Future of Regenerative Medicine
As biotechnology continues to advance, the role of amniotic tissue in medicine is expanding rapidly. Next-generation amniotic grafts and amniotic membrane allografts are being engineered with improved preservation techniques to maintain more of their native biological activity. Researchers are also investigating ways to integrate amniotic materials into 3D-printed scaffolds and nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems.
In the future, these innovations may allow doctors to not only heal damaged tissues but also restore their original function — bridging the gap between repair and true regeneration.
Conclusion
The use of amniotic grafts and amniotic membrane allografts marks a new era in regenerative medicine. By combining biological compatibility with powerful healing properties, these advanced therapies are helping patients recover faster, experience less pain, and achieve better long-term outcomes.
From chronic wound management to surgical recovery and tissue engineering, amniotic-based solutions are redefining how medicine approaches healing — naturally, effectively, and safely. As research and technology evolve, these biologic innovations will continue to shape the future of modern healthcare, offering hope for millions of patients in need of regenerative treatment.